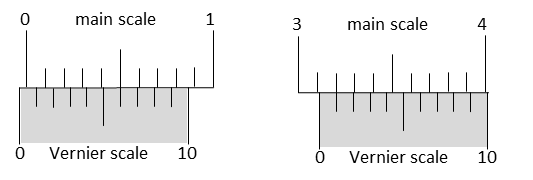
JEE Advanced 2021
Paper 1
- This section contains FOUR (04) questions.
- Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is the correct answer.
- Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen.
- Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered).
- Negative Marks : −1 In all other cases.


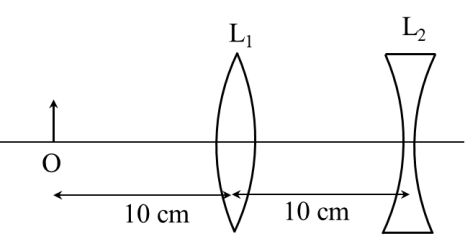
- This section contains THREE (03) question stems.
- There are TWO (02) questions corresponding to each question stem.
- The answer to each question is a NUMERICAL VALUE.
- If the numerical value has more than two decimal places, truncate/round-off the value to TWO decimal places.
- Full Marks : +2 If ONLY the correct numerical value is entered.
- Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
Question Stem for Question Nos. 5 and 6
A projectile is thrown from a point O on the ground at an angle 45° from the vertical and with a speed $5\sqrt{2}$ m/s. The projectile at the highest point of its trajectory splits into two equal parts. One part falls vertically down to the ground, 0.5 s after the splitting. The other part, $t$ seconds after the splitting, falls to the ground at a distance $x$ meters from the point O. The acceleration due to gravity $g = 10 \text{ m/s}^2$.
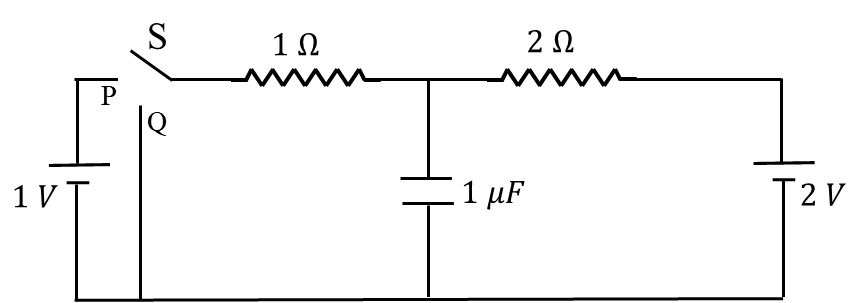
Question Stem for Question Nos. 7 and 8
In the circuit shown below, the switch S is connected to position P for a long time so that the
charge on the capacitor becomes $q_1$ µC. Then S is switched to position Q. After a long time, the
charge on the capacitor is $q_2$ µC.
Question Stem for Question Nos. 9 and 10
Two point charges $-Q$ and $+Q/\sqrt{3}$ are placed in the $xy$-plane at the origin $(0, 0)$ and a
point $(2, 0)$, respectively, as shown in the figure. This results in an equipotential circle of
radius $R$ and potential $V = 0$ in the $xy$-plane with its center at $(b, 0)$. All lengths are
measured in meters.

- This section contains SIX (06) questions.
- Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four options is(are) correct answer(s).
- Full Marks : +4 If only (all) the correct option(s) is(are) chosen.
- Partial Marks : +3 If all four options are correct but ONLY three are chosen.
- Partial Marks : +2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two are chosen, both correct.
- Partial Marks : +1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one is chosen and it is correct.
- Zero Marks : 0 If unanswered.
- Negative Marks : −2 In all other cases.
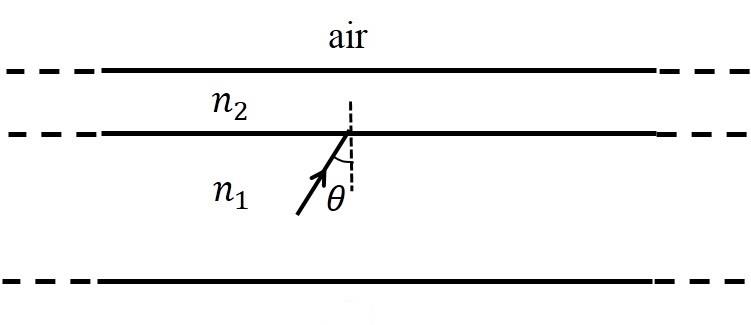


- This section contains THREE (03) questions.
- The answer to each question is a NON-NEGATIVE INTEGER.
- Full Marks : +4 If ONLY the correct integer is entered.
- Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
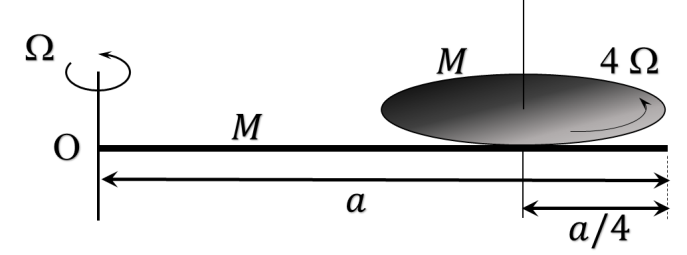
- This section contains FOUR (04) questions.
- Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is the correct answer.
- Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen.
- Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen.
- Negative Marks : -1 In all other cases.
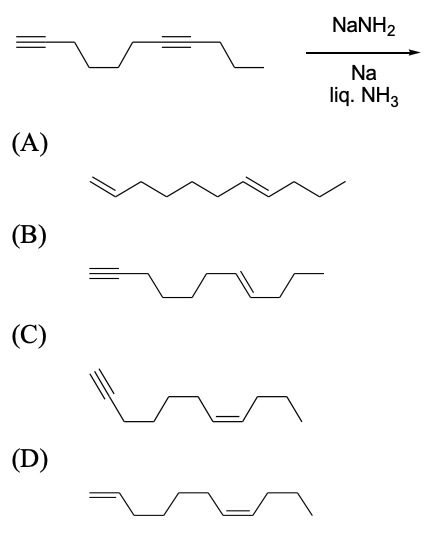
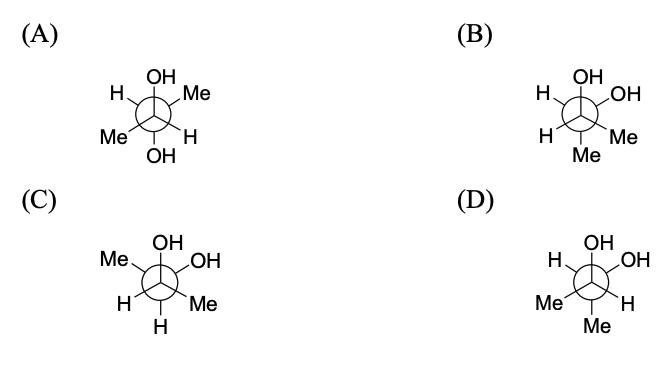
$$(\text{packing fraction} = \frac{\text{packing efficiency}}{100})$$
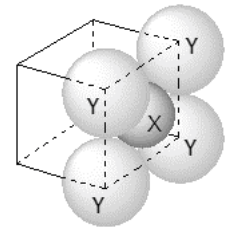
(Atomic numbers of Cr and Cu are 24 and 29, respectively)
- This section contains THREE (03) question stems.
- There are TWO (02) questions corresponding to each question stem.
- The answer to each question is a NUMERICAL VALUE.
- Truncate/round-off the value to TWO decimal places.
- Full Marks : +2 If ONLY the correct numerical value is entered.
- Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
Question Stem for Question Nos. 5 and 6
For the following reaction scheme, percentage yields are given along the arrow:
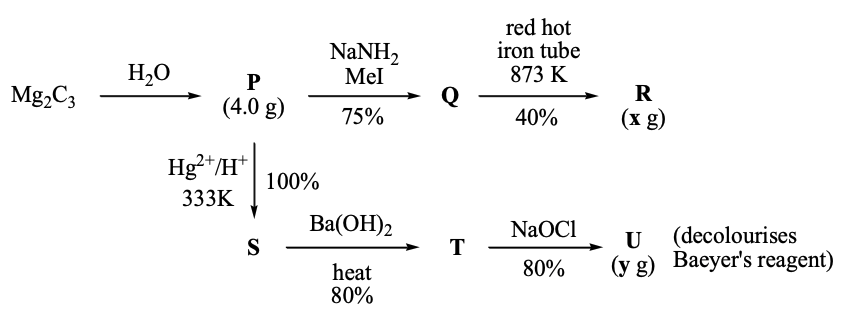
$x$ g and $y$ g are mass of R and U, respectively.
(Use: Molar mass (in g mol$^{-1}$) of H, C and O as 1, 12 and 16, respectively)
Question Stem for Question Nos. 7 and 8
For the reaction, $\mathbf{X}(s) \rightleftharpoons \mathbf{Y}(s) + \mathbf{Z}(g)$, the plot of $\ln \frac{p_Z}{p^\circ}$ versus $\frac{10^4}{T}$ is given below (in solid line), where $p_Z$ is the pressure (in bar) of the gas $\mathbf{Z}$ at temperature $T$ and $p^\circ = 1$ bar.
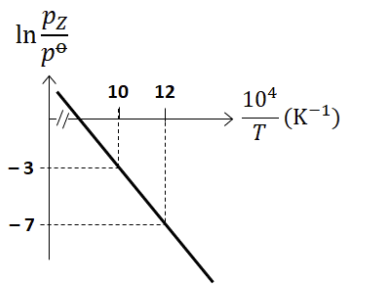
(Given, $\frac{d(\ln K)}{d(\frac{1}{T})} = -\frac{\Delta H^\circ}{R}$, where the equilibrium constant, $K = \frac{p_Z}{p^\circ}$ and the gas constant, $R = 8.314 \text{ J K}^{-1} \text{ mol}^{-1}$)
Question Stem for Question Nos. 9 and 10
The boiling point of water in a 0.1 molal silver nitrate solution (solution A) is $x^\circ$C. To this solution A, an equal volume of 0.1 molal aqueous barium chloride solution is added to make a new solution B. The difference in the boiling points of water in the two solutions A and B is $y \times 10^{-2} {}^\circ$C.
(Assume: Densities of the solutions A and B are the same as that of water and the soluble salts dissociate completely. Use: Molal elevation constant (Ebullioscopic Constant), $K_b = 0.5 \text{ K kg mol}^{-1}$; Boiling point of pure water as $100^\circ$C.)
- This section contains SIX (06) questions.
- ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of the options is correct.
- Full Marks : +4 If only (all) the correct option(s) is(are) chosen.
- Partial Marks : +3, +2, +1 (See detailed rules in PDF).
- Negative Marks : -2 In all other cases.
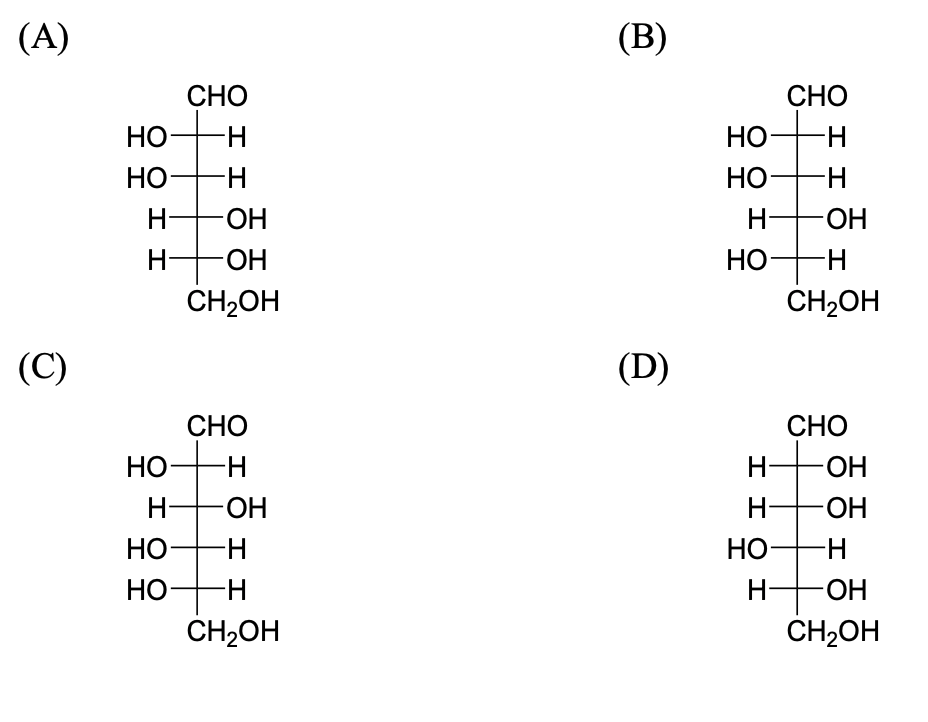
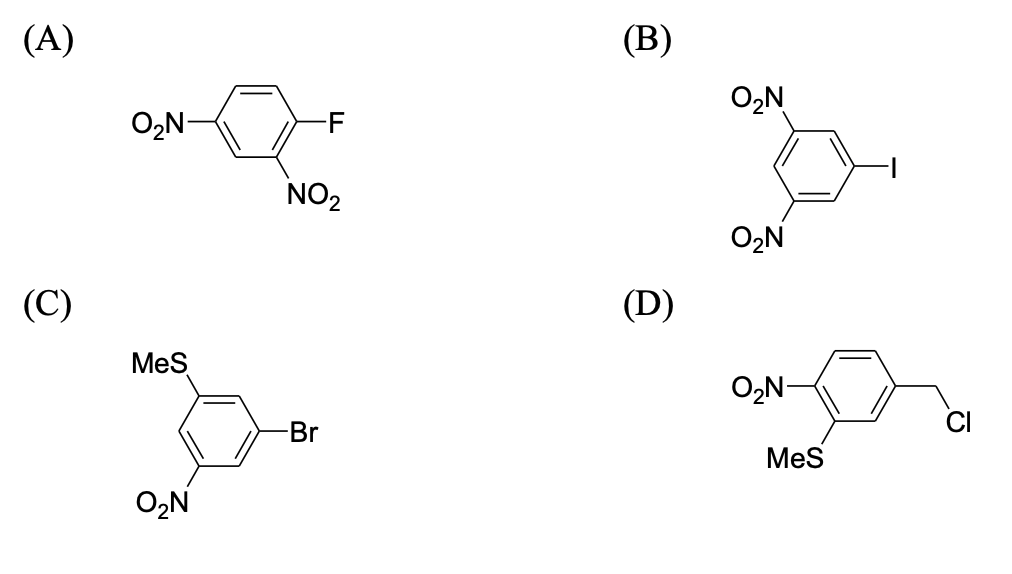
 The compound(s), which on reaction with HNO$_3$ will give the product having degree of rotation, $[\alpha]_D = -52.7^\circ$ is(are):
The compound(s), which on reaction with HNO$_3$ will give the product having degree of rotation, $[\alpha]_D = -52.7^\circ$ is(are):
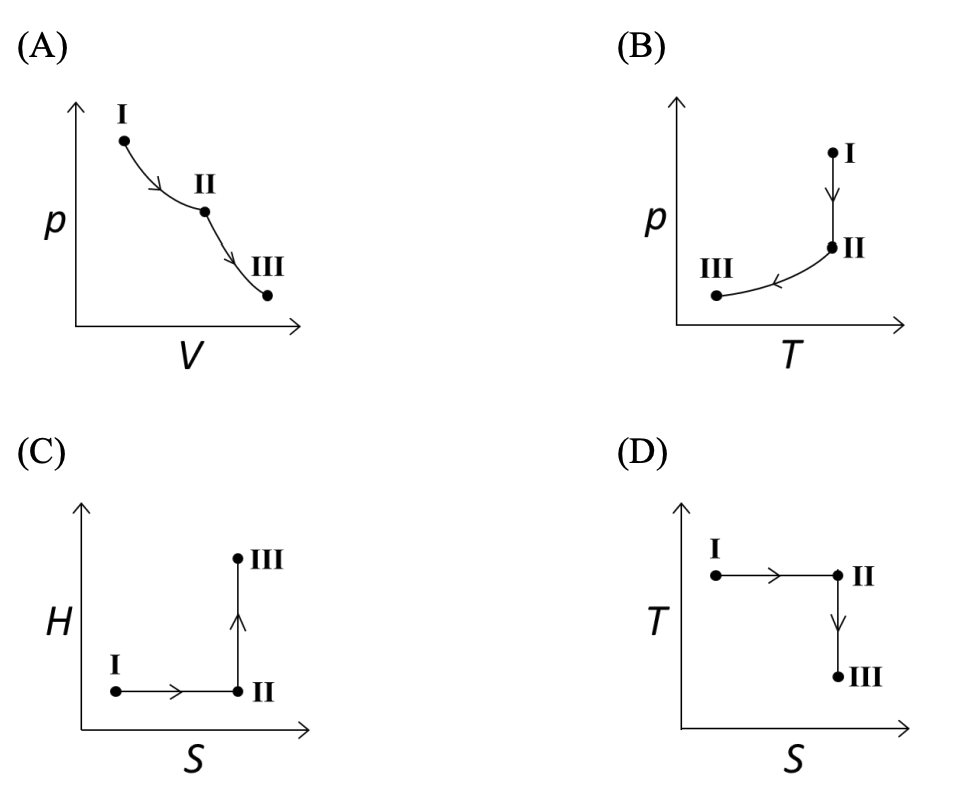
($p$: pressure, $V$: volume, $T$: temperature, $H$: enthalpy, $S$: entropy)
 The correct option(s) for the salt mixture is(are)
The correct option(s) for the salt mixture is(are)
- This section contains THREE (03) questions.
- The answer to each question is a NON-NEGATIVE INTEGER.
- Full Marks : +4 If ONLY the correct integer is entered.
- Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
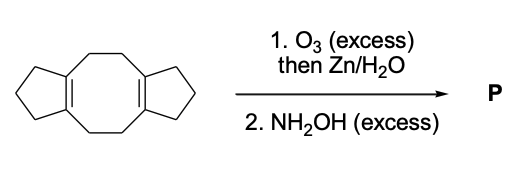
- This section contains FOUR (04) questions.
- Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is the correct answer.
- Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen;
- Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
- Negative Marks : −1 In all other cases.
Let $G_2 = G_1 \cup S_2$. Finally, two elements are chosen at random, without replacement, from the set $G_2$ and let $S_3$ denote the set of these chosen elements.
Let $E_3 = E_2 \cup S_3$. Given that $E_1 = E_3$, let $p$ be the conditional probability of the event $S_1 = \{1, 2\}$. Then the value of $p$ is
$P : |z_2 - z_1| + |z_3 - z_2| + \dots + |z_{10} - z_9| + |z_1 - z_{10}| \le 2\pi$
$Q : |z_2^2 - z_1^2| + |z_3^2 - z_2^2| + \dots + |z_{10}^2 - z_9^2| + |z_1^2 - z_{10}^2| \le 4\pi$
Then,
- This section contains THREE (03) question stems.
- There are TWO (02) questions corresponding to each question stem.
- The answer to each question is a NUMERICAL VALUE.
- If the numerical value has more than two decimal places, truncate/round-off the value to TWO decimal places.
- Full Marks : +2 If ONLY the correct numerical value is entered;
- Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
Three numbers are chosen at random, one after another with replacement, from the set $S = \{1, 2, 3, \dots, 100\}$. Let $p_1$ be the probability that the maximum of chosen numbers is at least 81 and $p_2$ be the probability that the minimum of chosen numbers is at most 40.
The value of $\frac{625}{4} p_1$ is ___.
Three numbers are chosen at random, one after another with replacement, from the set $S = \{1, 2, 3, \dots, 100\}$. Let $p_1$ be the probability that the maximum of chosen numbers is at least 81 and $p_2$ be the probability that the minimum of chosen numbers is at most 40.
The value of $\frac{125}{4} p_2$ is ____.
Let $\alpha, \beta$ and $\gamma$ be real numbers such that the system of linear equations $$ \begin{aligned} x + 2y + 3z &= \alpha \\ 4x + 5y + 6z &= \beta \\ 7x + 8y + 9z &= \gamma - 1 \end{aligned} $$ is consistent. Let $|M|$ represent the determinant of the matrix $$ M = \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 2 & \gamma \\ \beta & 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} $$ Let $P$ be the plane containing all those $(\alpha, \beta, \gamma)$ for which the above system of linear equations is consistent, and $D$ be the square of the distance of the point $(0, 1, 0)$ from the plane $P$.
The value of $|M|$ is ___.
Let $\alpha, \beta$ and $\gamma$ be real numbers such that the system of linear equations $$ \begin{aligned} x + 2y + 3z &= \alpha \\ 4x + 5y + 6z &= \beta \\ 7x + 8y + 9z &= \gamma - 1 \end{aligned} $$ is consistent. Let $|M|$ represent the determinant of the matrix $$ M = \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 2 & \gamma \\ \beta & 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} $$ Let $P$ be the plane containing all those $(\alpha, \beta, \gamma)$ for which the above system of linear equations is consistent, and $D$ be the square of the distance of the point $(0, 1, 0)$ from the plane $P$.
The value of $D$ is ___.
Consider the lines $L_1$ and $L_2$ defined by $$ L_1 : x\sqrt{2} + y - 1 = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad L_2 : x\sqrt{2} - y + 1 = 0 $$ For a fixed constant $\lambda$, let $C$ be the locus of a point $P$ such that the product of the distance of $P$ from $L_1$ and the distance of $P$ from $L_2$ is $\lambda^2$. The line $y = 2x + 1$ meets $C$ at two points $R$ and $S$, where the distance between $R$ and $S$ is $\sqrt{270}$.
Let the perpendicular bisector of $RS$ meet $C$ at two distinct points $R'$ and $S'$. Let $D$ be the square of the distance between $R'$ and $S'$.
The value of $\lambda^2$ is ___.
Consider the lines $L_1$ and $L_2$ defined by $$ L_1 : x\sqrt{2} + y - 1 = 0 \quad \text{and} \quad L_2 : x\sqrt{2} - y + 1 = 0 $$ For a fixed constant $\lambda$, let $C$ be the locus of a point $P$ such that the product of the distance of $P$ from $L_1$ and the distance of $P$ from $L_2$ is $\lambda^2$. The line $y = 2x + 1$ meets $C$ at two points $R$ and $S$, where the distance between $R$ and $S$ is $\sqrt{270}$.
Let the perpendicular bisector of $RS$ meet $C$ at two distinct points $R'$ and $S'$. Let $D$ be the square of the distance between $R'$ and $S'$.
The value of $D$ is ___.
- This section contains SIX (06) questions.
- Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four option(s) is (are) correct answer(s).
- Full Marks : +4 If only (all) the correct option(s) is(are) chosen;
- Partial Marks : +3 If all the four options are correct but ONLY three options are chosen;
- Partial Marks : +2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two options are chosen, both of which are correct;
- Partial Marks : +1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it is a correct option;
- Zero Marks : 0 If unanswered;
- Negative Marks : −2 In all other cases.
- This section contains THREE (03) questions.
- The answer to each question is a NON-NEGATIVE INTEGER.
- Full Marks : +4 If ONLY the correct integer is entered;
- Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.