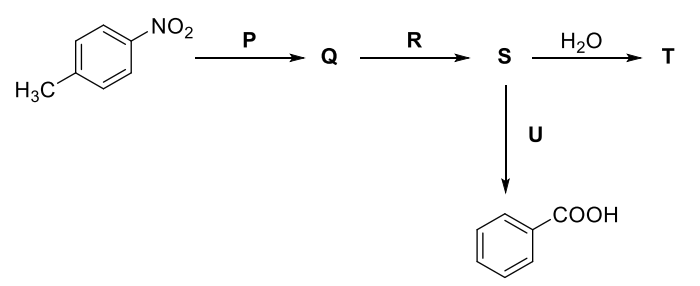
Q.1
Considering only the principal values of the inverse trigonometric functions, the value of
$$ \frac{3}{2} \cos^{-1} \sqrt{\frac{2}{2 + \pi^2}} + \frac{1}{4} \sin^{-1} \frac{2\sqrt{2}
\pi}{2 + \pi^2} + \tan^{-1} \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\pi} $$
is __________.
2.35 or 2.36
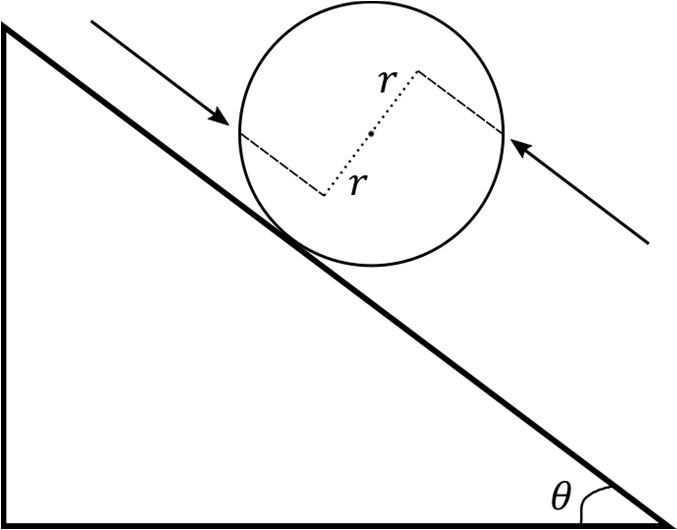
 In the process of going from the configuration depicted in Figure (a) to that in Figure (b),
which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
In the process of going from the configuration depicted in Figure (a) to that in Figure (b),
which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
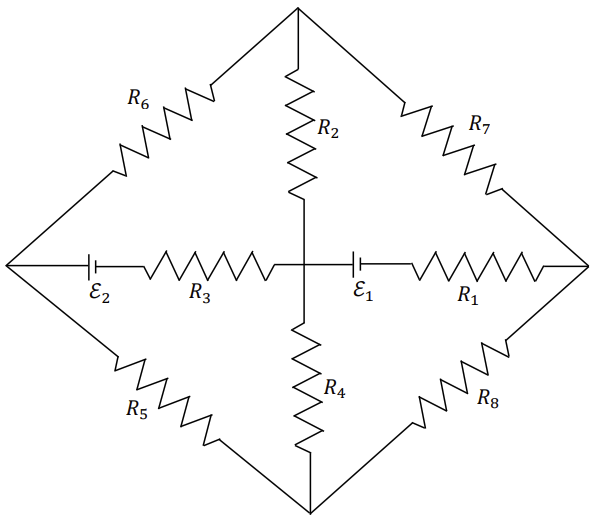 Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
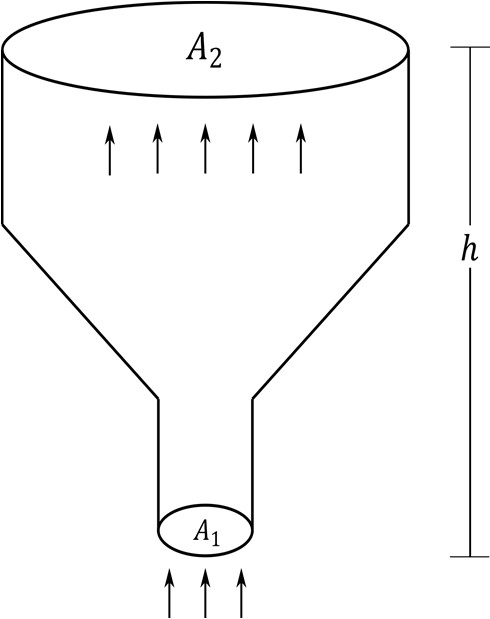 Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
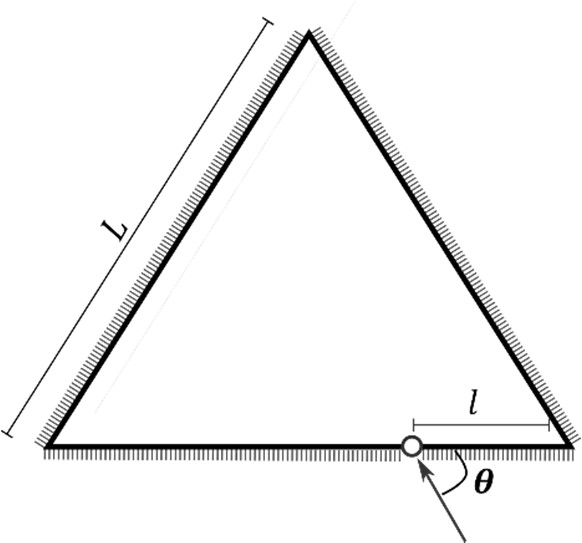 Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
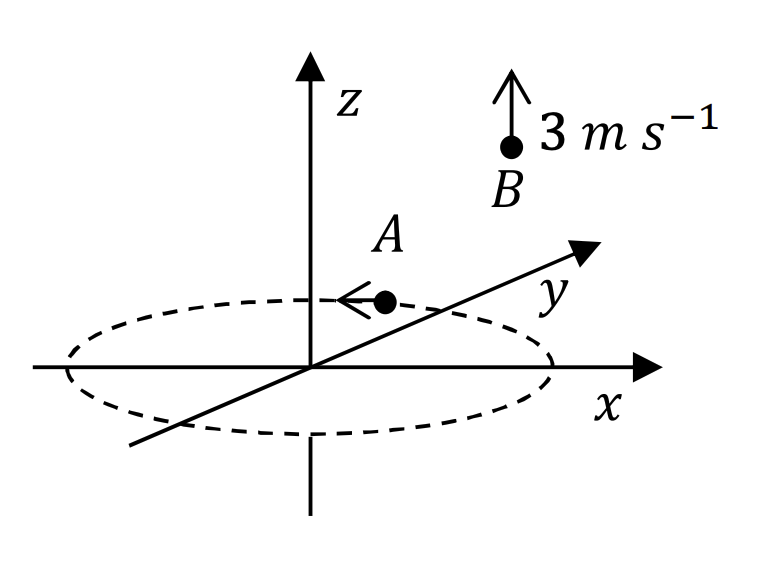
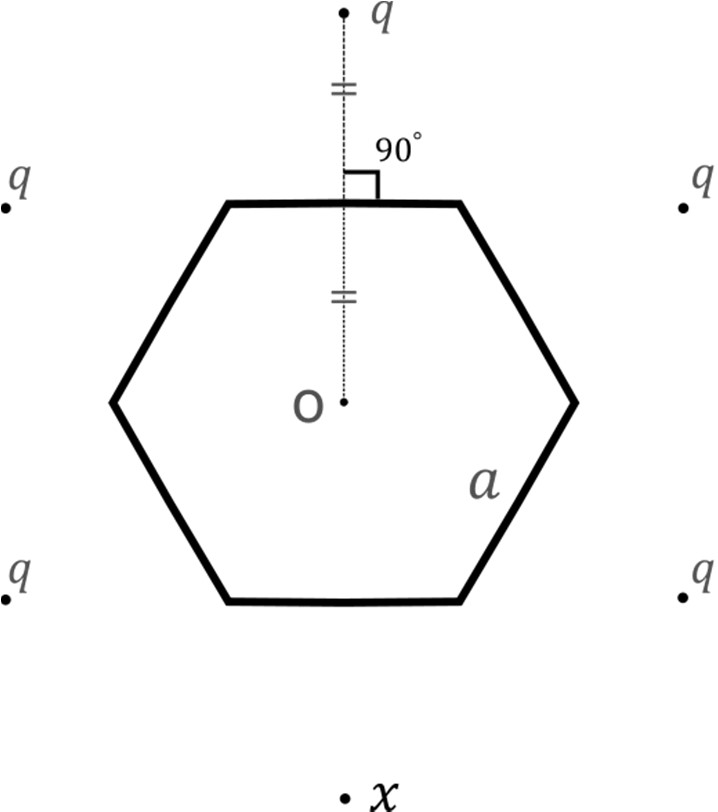 Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct in SI units?
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct in SI units?
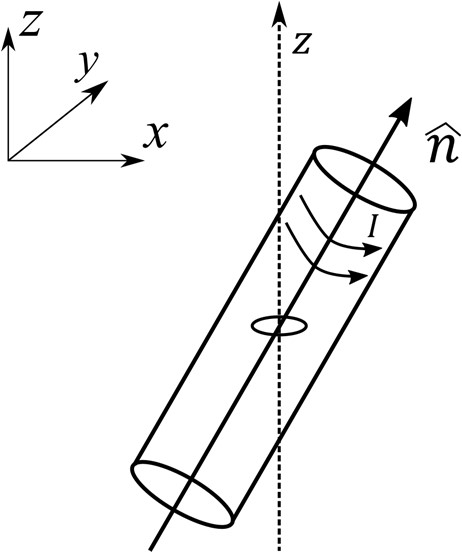
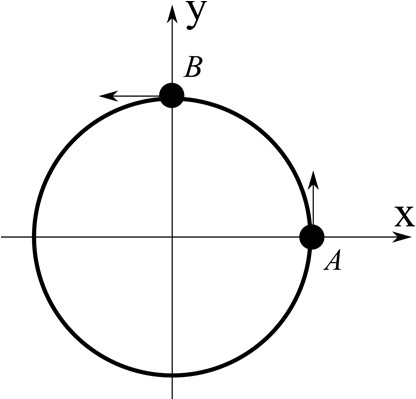
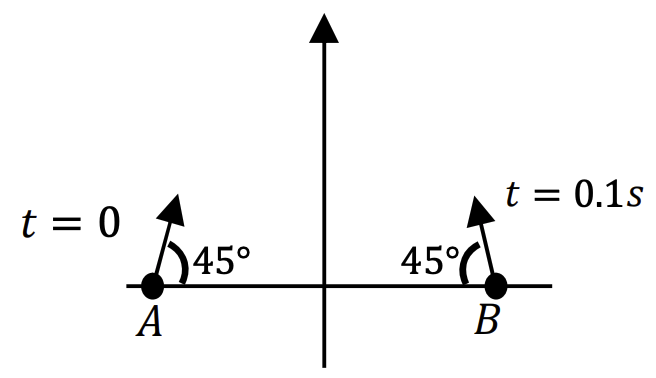

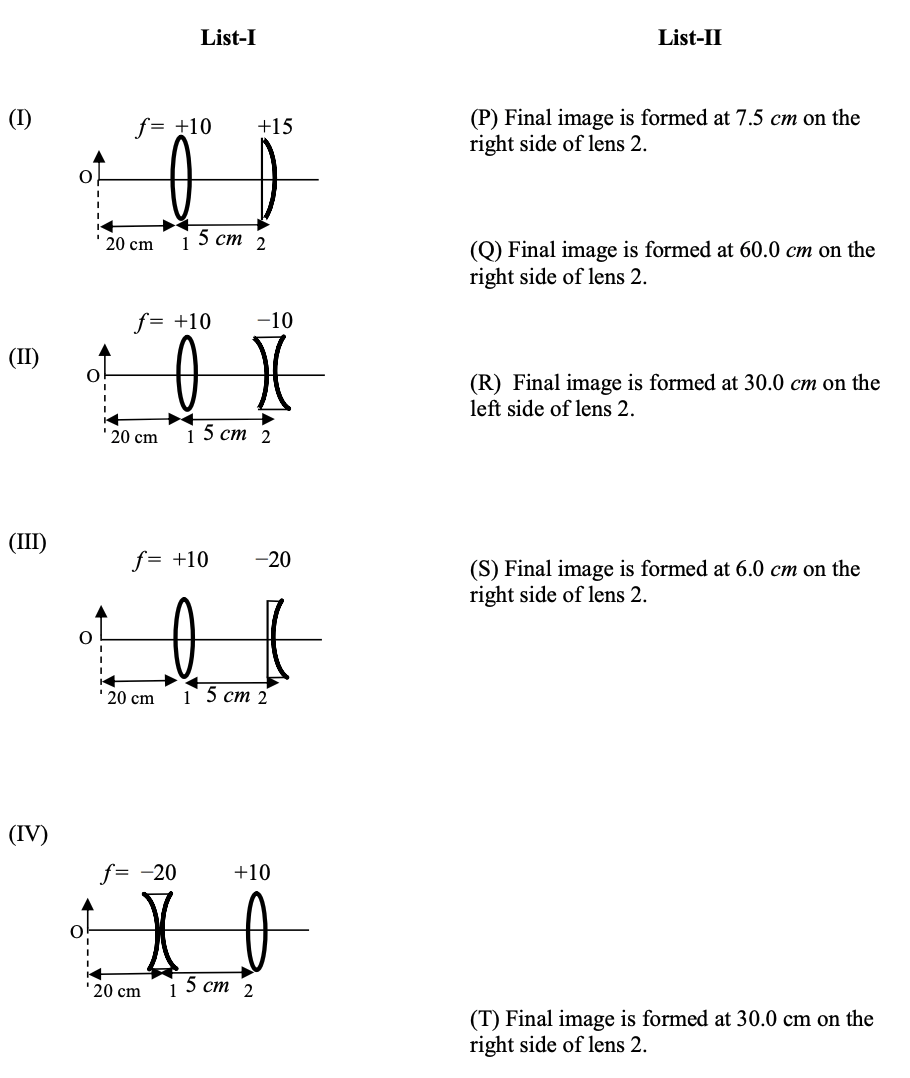 Which one of the following options is correct?
Which one of the following options is correct?
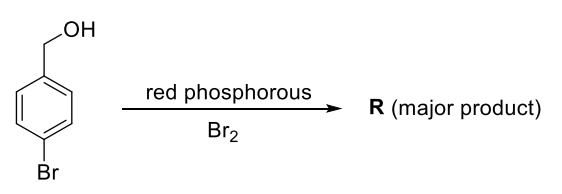 On estimation of bromine in 1.00 g of R using Carius method, the amount of AgBr formed (in g) is ________.
On estimation of bromine in 1.00 g of R using Carius method, the amount of AgBr formed (in g) is ________.
 [Given: Atomic mass of H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O = 16, S = 32, Cl = 35]
[Given: Atomic mass of H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O = 16, S = 32, Cl = 35]
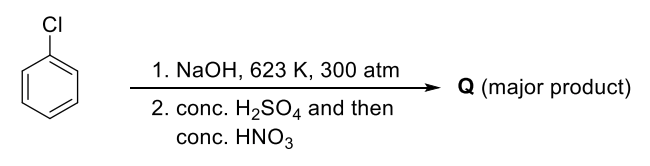
 The yields of A, B, C and D are given in parentheses.
The yields of A, B, C and D are given in parentheses.