Solution
Step 1: Apply Newton-Leibniz Theorem
The given integral equation is:
$$ 3\int_{1}^{x} f(t) dt = x f(x) - \frac{x^3}{3} $$
Differentiating both sides with respect to \( x \) using the Newton-Leibniz theorem:
$$ \frac{d}{dx}\left( 3\int_{1}^{x} f(t) dt \right) = \frac{d}{dx}\left( x f(x) - \frac{x^3}{3} \right) $$
$$ 3 f(x) = \left( 1 \cdot f(x) + x f'(x) \right) - x^2 $$
$$ 3 f(x) = f(x) + x f'(x) - x^2 $$
Rearranging the terms, we get:
$$ 2 f(x) = x f'(x) - x^2 $$
$$ x \frac{dy}{dx} - 2y = x^2 $$
$$ \frac{dy}{dx} - \frac{2}{x}y = x $$
This is a linear differential equation of the form \( \frac{dy}{dx} + P(x)y = Q(x) \), where \( P(x) = -\frac{2}{x} \) and \( Q(x) = x \).
Step 2: Find the Integrating Factor (I.F.)
$$ \text{I.F.} = e^{\int P(x) dx} = e^{\int -\frac{2}{x} dx} = e^{-2 \ln x} = e^{\ln(x^{-2})} = \frac{1}{x^2} $$
Step 3: Solve the Differential Equation
Multiplying the differential equation by the I.F.:
$$ y \cdot (\text{I.F.}) = \int Q(x) \cdot (\text{I.F.}) dx + C $$
$$ y \cdot \frac{1}{x^2} = \int x \cdot \frac{1}{x^2} dx + C $$
$$ \frac{y}{x^2} = \int \frac{1}{x} dx + C $$
$$ \frac{y}{x^2} = \ln x + C $$
$$ y = x^2 \ln x + C x^2 $$
Step 4: Use Initial Condition to Find C
Given \( f(1) = \frac{1}{3} \). Substituting \( x = 1 \) and \( y = 1/3 \):
$$ \frac{1}{3} = 1^2 \cdot \ln(1) + C(1)^2 $$
Since \( \ln(1) = 0 \):
$$ \frac{1}{3} = 0 + C \Rightarrow C = \frac{1}{3} $$
So, the function is:
$$ f(x) = x^2 \ln x + \frac{1}{3} x^2 $$
Step 5: Find \( f(e) \)
Substitute \( x = e \):
$$ f(e) = e^2 \ln e + \frac{1}{3} e^2 $$
Since \( \ln e = 1 \):
$$ f(e) = e^2(1) + \frac{1}{3} e^2 = e^2 + \frac{e^2}{3} = \frac{4e^2}{3} $$
Correct Option: (C)
Option Distractor Reasons
Likely result of an algebraic error in adding terms, possibly obtaining \( \frac{e^2+4}{3} \) by miscalculating constants.
Incorrect integration of \( 1/x \) or logarithmic manipulation error leading to a form with \( \log_e 4 \).
Result of a sign error when evaluating the constant \( C \) or subtracting terms at the end.
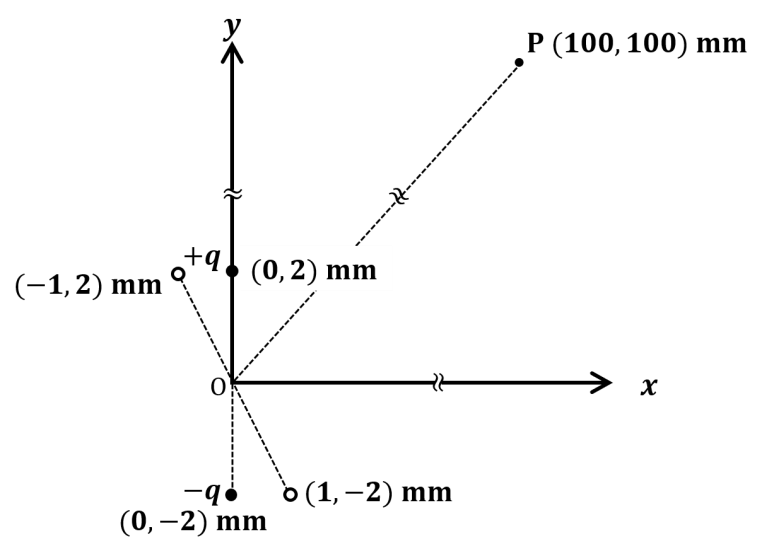
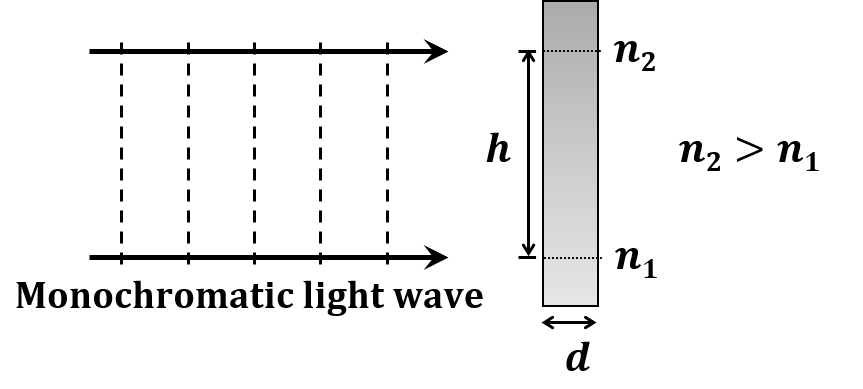
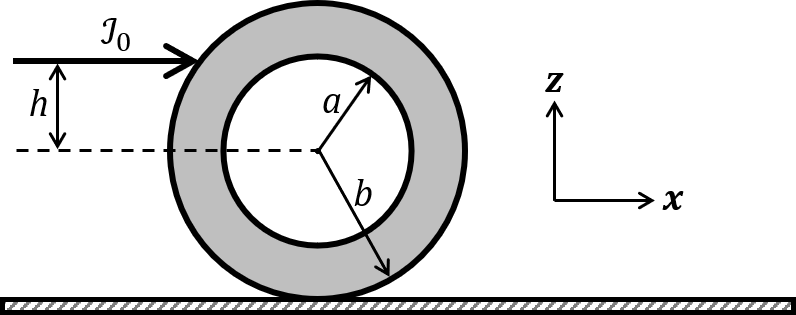
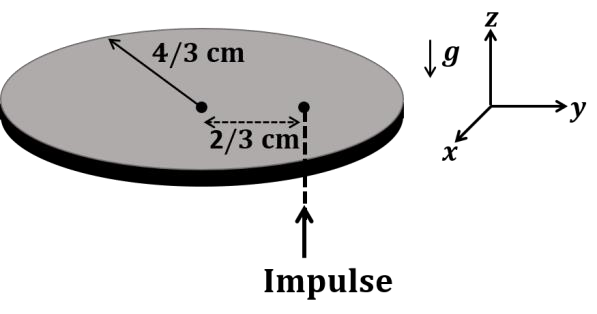
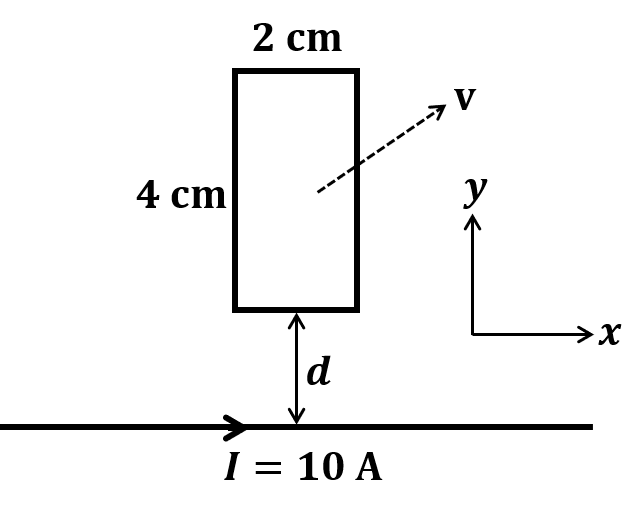
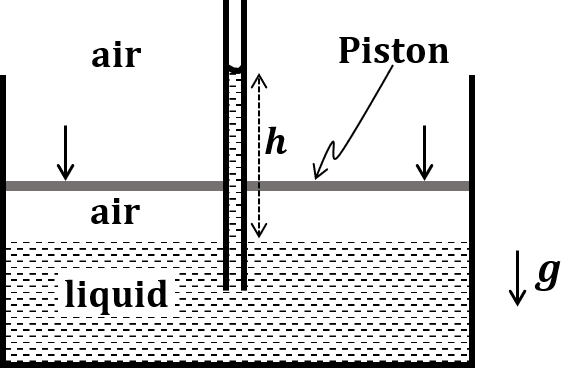
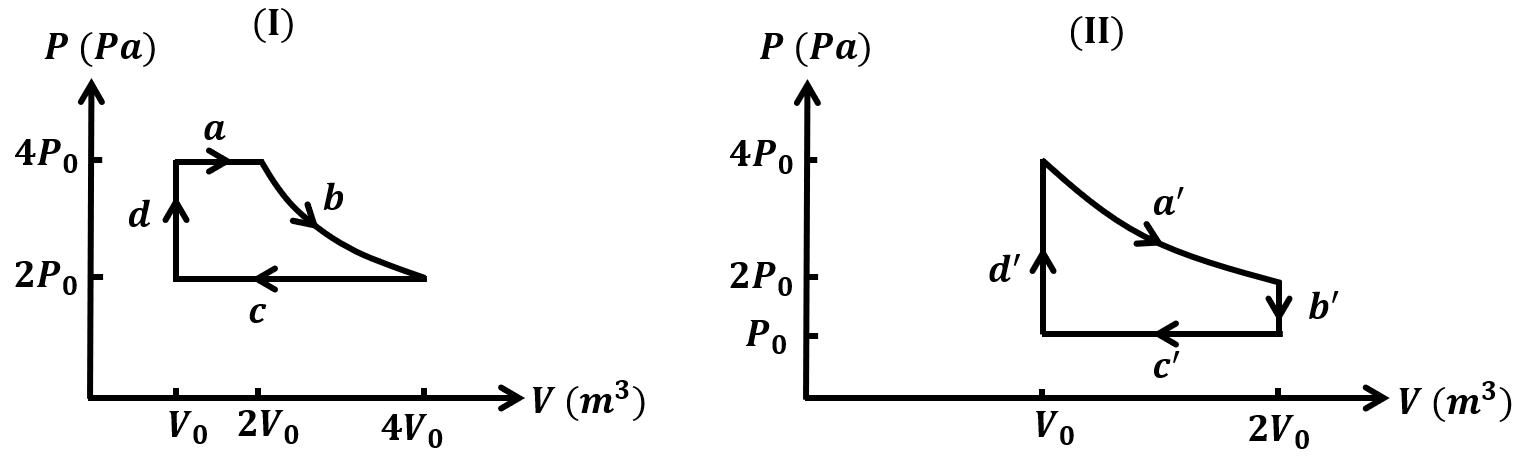
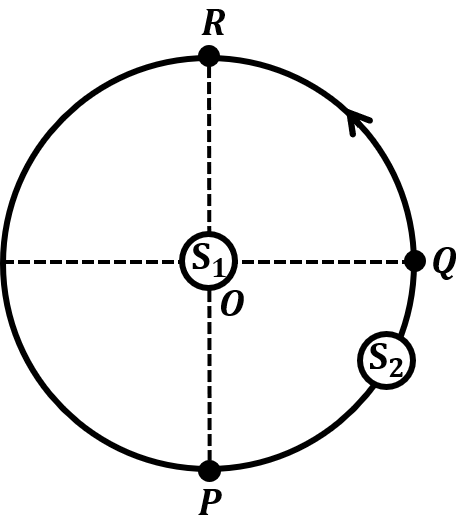
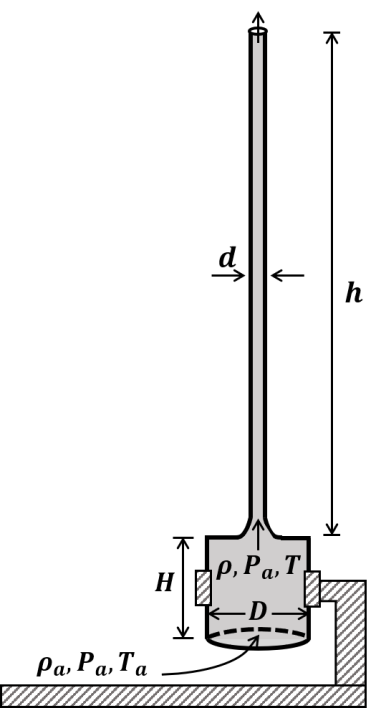
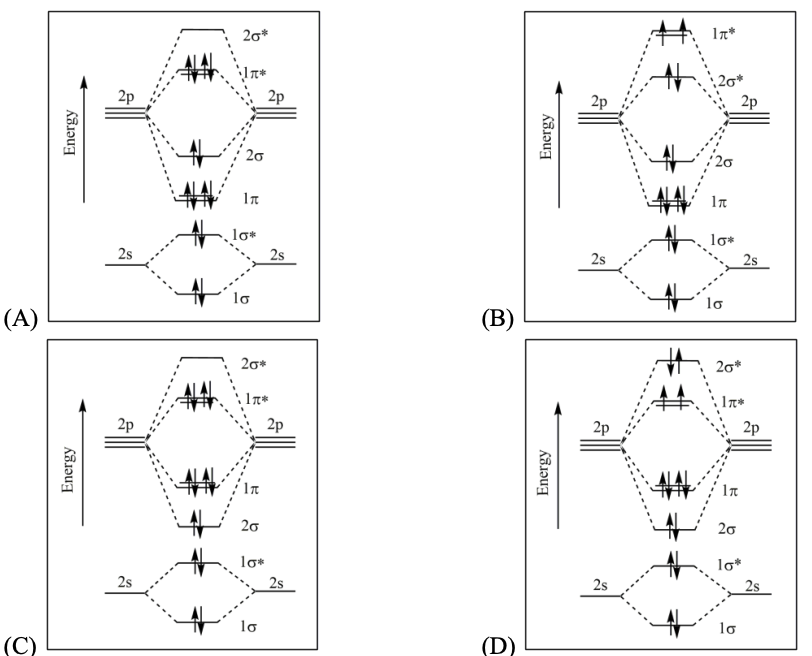
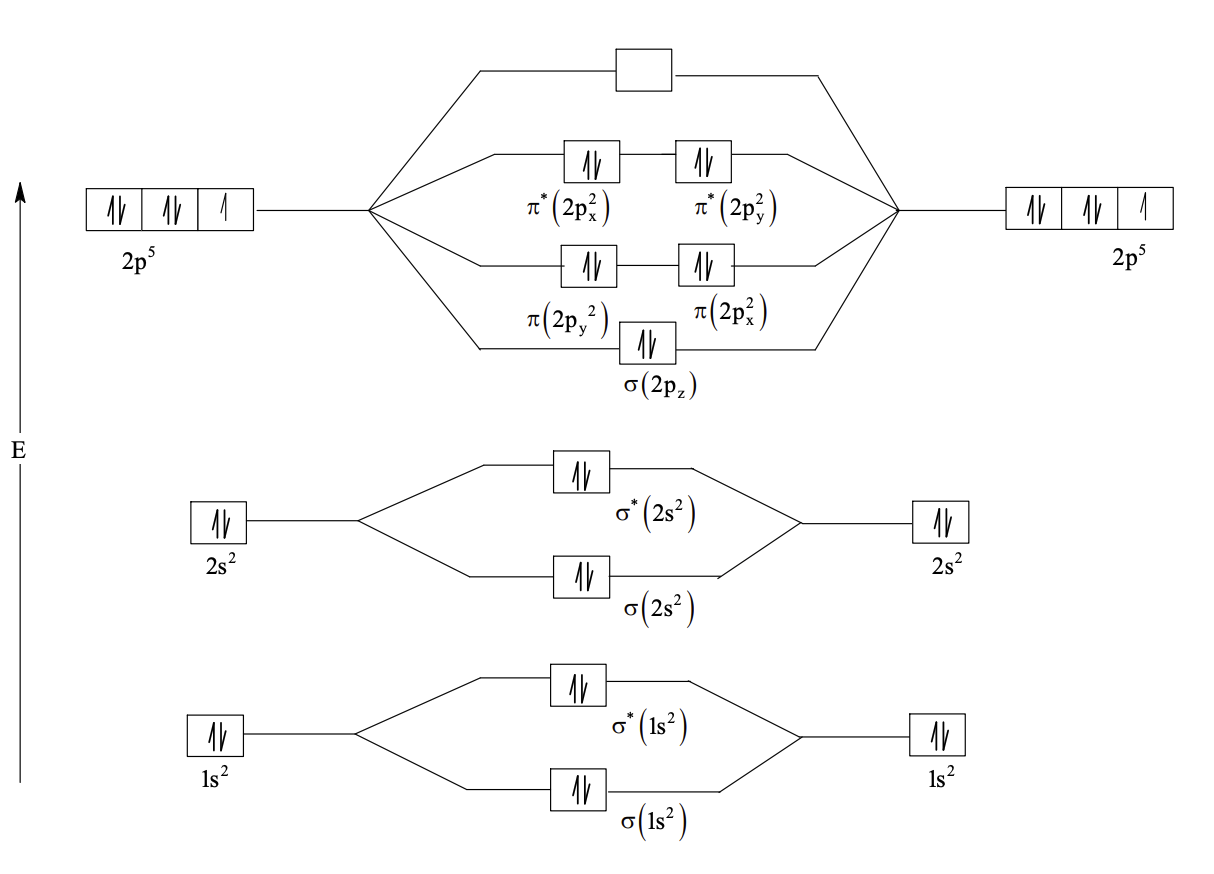
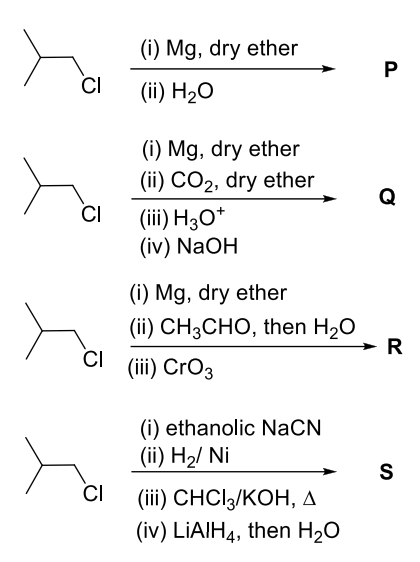 The correct statement about P, Q, R, and S is
The correct statement about P, Q, R, and S is
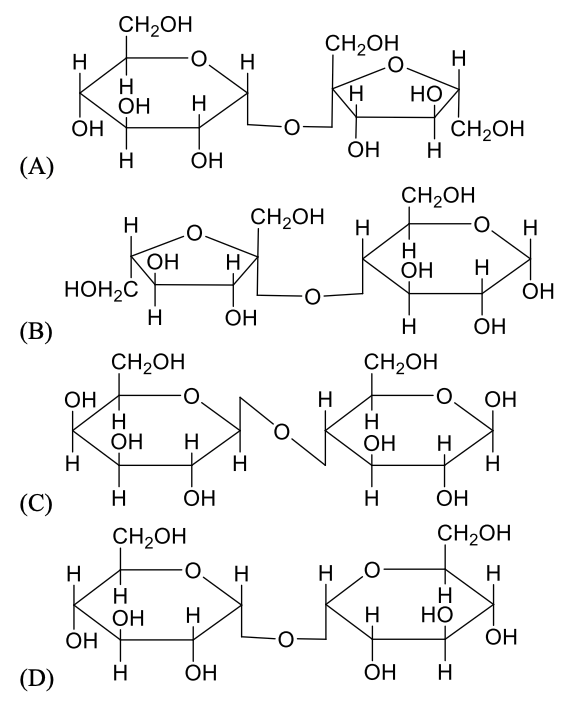
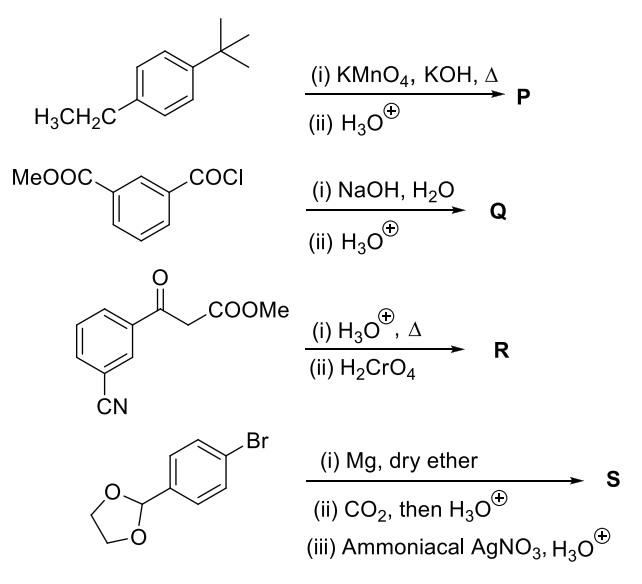 The correct statement(s) about P, Q, R, and S is(are)
The correct statement(s) about P, Q, R, and S is(are)